Upper Extremity Orthoses
Upper Extremity Orthoses
Upper Extremity Orthoses are orthopedic devices used to support function, limit movement, and speed up the healing process after injuries, diseases, or surgeries in body parts such as the arm, hand, shoulder, elbow, and wrist. These orthoses are commonly used for trauma, muscle weakness, joint problems, or neurological disorders. Upper extremity orthoses stabilize the body part, reduce pain, and support recovery.
Types of Upper Extremity Orthoses:
Wrist Orthoses (Wrist Orthosis)
Indications: Wrist sprains, wrist dislocations, tendon injuries, carpal tunnel syndrome, and similar conditions.
Features: Orthoses that stabilize the wrist, limit its movement, and support the healing process. Typically made of elastic, lightweight, and comfortable materials.
Example: Wrist splint used for treating carpal tunnel syndrome.
Elbow Orthoses (Elbow Orthosis)
Indications: Elbow dislocations, fractures, tendon injuries, and post-surgical stabilization.
Features: Devices designed to restrict movement and provide stability to the elbow joint. Usually include hinge mechanisms and may be adjustable to limit or control the range of motion.
Example: Elbow splint: Used to immobilize the elbow and assist in healing.
Shoulder Orthoses (Shoulder Orthosis)
Indications: Shoulder dislocations, fractures, post-shoulder surgery, or muscle weakness.
Features: Stabilizes the shoulder joint to reduce pain and support recovery. Limits shoulder movements to prevent excessive strain.
Example: Shoulder abduction orthosis: Limits outward movement of the shoulder to speed up healing in shoulder injuries.
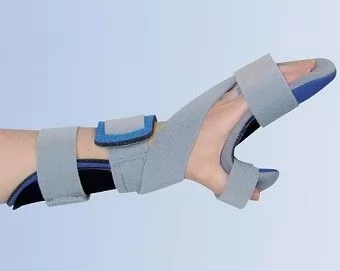
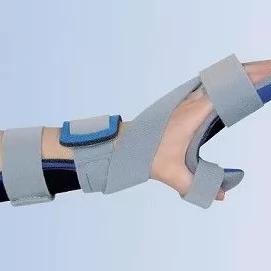
Hand Orthoses (Hand Orthosis)
Indications: Hand injuries, finger fractures, paralysis, or neurological disorders causing loss of hand function.
Features: Helps improve hand function by limiting movement or maintaining specific positions, usually targeting fingers and wrist.
Example: Finger splint: Immobilizes fingers during fractures or injuries to support healing.
Arm Orthoses (Arm Orthosis)
Indications: Arm fractures, shoulder and elbow injuries, muscle weakness, and post-surgical use.
Features: Limits arm movement to support healing. Some orthoses are designed to hold the arm in a fixed position.
Example: Arm sling: Keeps the arm stable in shoulder or arm injuries to accelerate healing.
Special Functional Orthoses
Indications: Orthoses targeting specific functions, such as finger prostheses, bionic hand orthoses, or motorized orthoses.
Features: Includes bionic systems or electric support mechanisms designed to improve hand or finger functions.
Example: Bionic hand orthosis: An orthosis supported by electronic components designed to improve hand movements for individuals with paralysis or disabilities.
Usage Areas:
- Injuries: To provide stability and assist healing after fractures and dislocations of the hand, wrist, elbow, or shoulder.
- Post-Surgical Rehabilitation: To accelerate recovery after shoulder, arm, hand, or wrist surgery.
- Muscle Weakness and Neurological Disorders: To support weakened muscles caused by diseases such as MS, cerebral palsy, or stroke.
- Joint Issues: To prevent movement restrictions in joint diseases like rheumatoid arthritis or arthritis.
Upper extremity orthoses help patients gain more independence in daily life and make significant contributions to the healing process. These orthoses can be custom-designed for each individual and are important tools to increase treatment effectiveness.